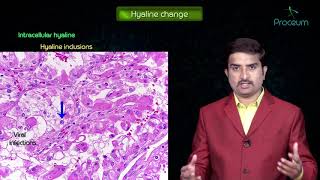
Cell adaptation within limits: Most cells have the ability to adapt to changes in their environment by altering their morphology, pattern of growth and metabolic activity. Common examples include: atrophy, hypertrophy, hyperplasia, metaplasia and dysplasia.
Hypertrophy: Hypertrophy refers to an increase in the physical size of cells. When hypertrophy occurs simultaneously in a population of adjacent cells this can lead to increased tissue or organ size.
Hyperplasia: Hyperplasia refers to an increase in the number of cells within a tissue due to mitosis.
Atrophy: Atrophy refers to a decrease in the physical size of cells. When atrophy occurs simultaneously in a population of adjacent cells this can lead to decreased tissue or organ size.
Metaplasia: Metaplasia refers to a reversible histological replacement of one differentiated cell type with another.
Dysplasia: The cells look abnormal under a microscope but are not cancer cells. Dysplasia refers to an abnormal and potentially reversible process where there is disordered growth and maturation of cells and the tissues and organs.