Understanding poisons and their antidotes is essential in pharmacy, medicine, and toxicology.
Many substances can cause life-threatening poisoning, and knowing the correct antidote,
dosage, and mechanism of action can save lives. This article provides detailed explanations
of 20 important poisons and their antidotes, followed by a simplified table for quick revision.
1. Arsenic Poison
Antidote: Dimercaprol (BAL). Administered intramuscularly at 2.5 mg/kg every 4 hours initially, then tapered. It binds with arsenic to form a complex excreted in urine. Detoxification may take 7–14 days.
2. Aconitine
Antidote: No specific antidote. Supportive care is given with antiarrhythmic drugs such as lidocaine via IV. Continuous monitoring is required as the drug stabilizes cardiac rhythm.
3. Batrachotoxin
Antidote: Activated charcoal and respiratory support. A single oral dose of 50–100 g charcoal absorbs toxin from the GI tract. Ventilation support may be needed to prevent respiratory failure.
4. Botulinum Toxin
Antidote: Botulinum Antitoxin. Given as a one-time IV infusion, it neutralizes circulating toxin molecules. Though symptoms may last weeks, progression is halted.
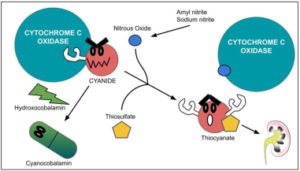
5. Cyanide
Antidote: Hydroxocobalamin (5 g IV) or Sodium Thiosulfate (12.5 g IV). Hydroxocobalamin binds cyanide, forming non-toxic cyanocobalamin. Thiosulfate converts cyanide into thiocyanate, excreted in urine.
6. Dimethylmercury
Antidote: Dimercaprol (BAL). Dose schedule is similar to arsenic poisoning. It binds mercury and enhances excretion, but treatment often lasts weeks to months due to mercury persistence in tissues.
7. Dimethylcadmium
Antidote: No specific antidote; chelation therapy with dimercaprol and supportive care is provided. Treatment continues for days to weeks depending on exposure severity.
8. Maitotoxin
Antidote: Supportive care with ventilation and IV fluids. There is no specific antidote, so management focuses on sustaining vital functions until the toxin clears (few days to a week).
9. Polonium-210
Antidote: Prussian Blue and Potassium Iodide, given orally. Prussian Blue binds radioactive particles in the gut, while potassium iodide protects the thyroid. Requires prolonged treatment (weeks to months).
10. Ricin
Antidote: No direct antidote. Activated charcoal (50–100 g) may be given if ingested, along with IV fluids for hydration. Care is supportive, lasting 1–2 weeks depending on severity.
11. Sarin
Antidote: Atropine (2 mg every 5–10 min) and Pralidoxime (600 mg every 15 min × 3 doses). Atropine blocks excess acetylcholine while pralidoxime reactivates acetylcholinesterase.
12. Tetrodotoxin
Antidote: No specific antidote. Treatment involves gastric lavage and mechanical ventilation until the toxin clears (24–48 hours).
13. VR Nerve Agent
Antidote: Atropine and Pralidoxime, similar to Sarin. Treatment continues until symptoms subside.
14. Heliotrope (Pyrrolizidine Alkaloids)
Antidote: No specific antidote. Symptomatic treatment supports liver function and prevents further damage. Recovery may take weeks to months.
15. Colchicine
Antidote: No specific antidote. Aggressive hydration is key, given orally or IV. Supportive care may last several days to weeks.
16. Cicutoxin (Water Hemlock)
Antidote: Benzodiazepines such as Diazepam (5–10 mg IV) or Lorazepam (4 mg IV), repeated every 5–10 min until seizures are controlled. Care usually lasts 24–48 hours.
17. Amatoxin (Amanita phalloides)
Antidote: Silibinin (20–50 mg/kg/day for 7 days) plus activated charcoal (50–100 g). Silibinin prevents uptake in liver cells, promotes regeneration, and reduces toxicity.
18. Amanita Virosa (Destroying Angel)
Antidote: Same as Amatoxin: Silibinin and activated charcoal. Management and mechanism are identical.
19. Thiopental / Pentobarbital (Barbiturates)
Antidote: No specific antidote. Activated charcoal (50–100 g) plus IV fluids for alkaline diuresis. Care continues for 24–48 hours.
20. Tetraethyl Lead
Antidote: Chelation therapy with Calcium Disodium EDTA (CaNa2EDTA). Given IV, 1000–1500 mg/m²/day in divided doses for 5 days, followed by rest and repeat if required.
Simplified Table for Quick Revision
| Toxin | Antidote | Administration & Dose |
|---|---|---|
| Arsenic | Dimercaprol (BAL) | 2.5 mg/kg IM q4h, tapered |
| Aconitine | Supportive (Lidocaine IV) | Dose varies, continuous monitoring |
| Batrachotoxin | Activated Charcoal | 50–100 g orally, respiratory support |
| Botulinum toxin | Botulinum Antitoxin | One-time IV infusion |
| Cyanide | Hydroxocobalamin / Sodium Thiosulfate | 5 g IV, 12.5 g IV |
| Dimethylmercury | Dimercaprol | 2.5 mg/kg IM q4h, long duration |
| Dimethylcadmium | Supportive + Chelation | Dose varies |
| Maitotoxin | Supportive care | Ventilation, IV fluids |
| Polonium-210 | Prussian Blue + KI | Daily oral doses, weeks–months |
| Ricin | Activated Charcoal | 50–100 g orally + IV fluids |
| Sarin / VR | Atropine + Pralidoxime | Atropine 2 mg q5–10 min; 2-PAM 600 mg |
| Tetrodotoxin | Supportive | Ventilation, 24–48 h |
| Heliotrope | Supportive care | Liver function support |
| Colchicine | Supportive care | Aggressive hydration |
| Cicutoxin | Benzodiazepines | Diazepam 5–10 mg IV |
| Amatoxin | Silibinin + Charcoal | Silibinin 20–50 mg/kg/day × 7 days |
| Amanita Virosa | Silibinin + Charcoal | Same as Amatoxin |
| Thiopental / Pentobarbital | Activated Charcoal | 50–100 g orally, IV fluids |
| Tetraethyl Lead | CaNa2EDTA | 1000–1500 mg/m²/day IV × 5 days |
Note: This article is for educational purposes only.
All antidotes and dosages must be administered under professional medical supervision.
The content is designed for pharmacy and medical students for toxicology reference.