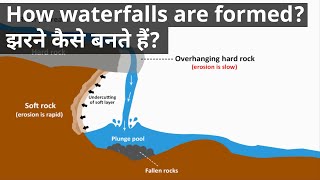
A Waterfall is a river or a body of water that steeply falls over a rocky edge into a plunge pool. These are also called cascades.
Waterfalls form as streams flow from soft rock to hard rock. This happens both laterally (as a stream flows across the earth) and vertically (as the stream drops in a waterfall). In both cases, the soft rock erodes, leaving a hard ledge over which the stream falls.
Waterfall formation is based around the basic principle that there is a watercourse (realize that water is an erosive agent) traversing over different layers of rock each with different rates of erosion.
The fall line is an imaginary line along which parallel rivers plunge while flowing from uplands to low lands. Many waterfalls in this way help the geologists determine a region’s fall line and underlying rock structure.
As the stream flows it carries various amounts of sediments- be it microscopic silt, pebbles or boulders. Sediments erode the beds of soft rocks like sandstone or limestone. The stream then cuts the beds so deep that only hard rocks like granite are left. Waterfalls develop as the granite formations form cliffs and ledges.
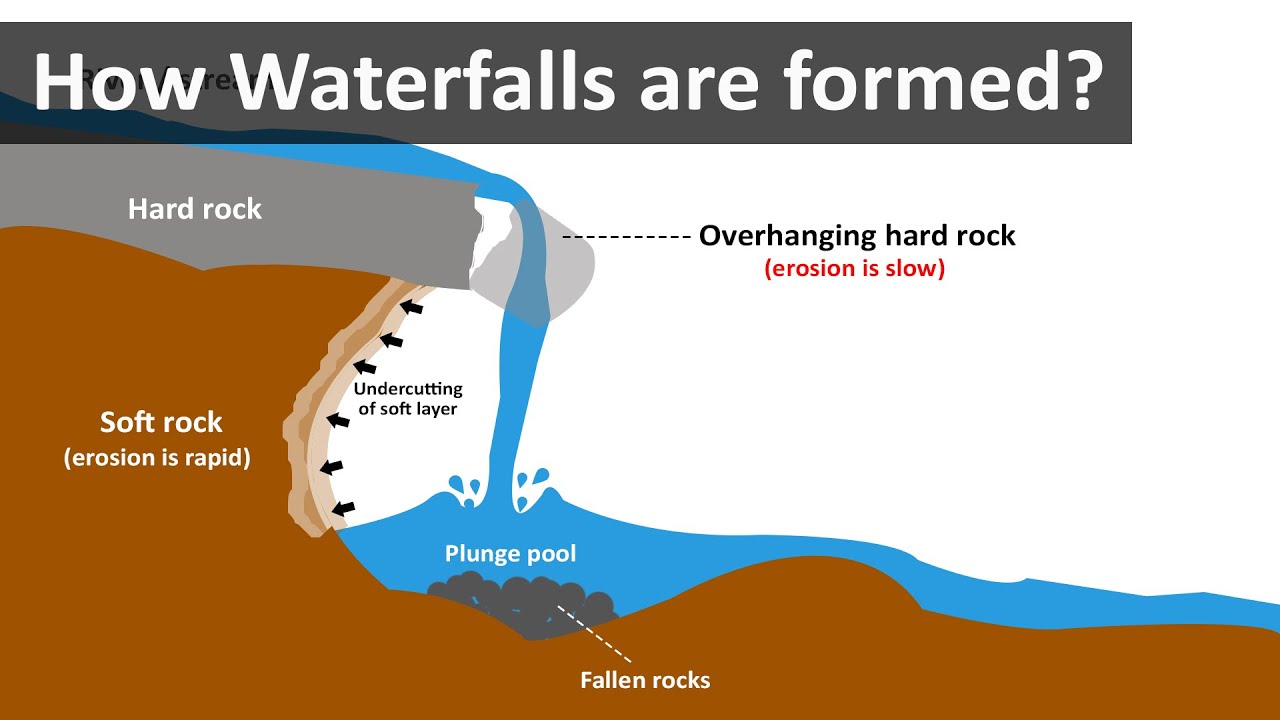
As the undercutting continues, eventually the overhanging hard rock becomes unstable and top heavy.
Ultimately, a chunk of that erosion-resistant hard rock layer collapses and falls into the base of the waterfall.
The net result of this action is that the waterfall retreats further upstream to the remaining lip of the hard rock layer.
The stream’s erosion increases near the base as velocity increases of the rivers. The movement of water at the top can erode the rocks to be flat and smooth. This way the plunge pool is formed at the base. The crashing flow also sometimes creates whirlpools that erode the plunge pool beneath them.
The erosion at the base of the waterfall causes the water to recede. The area behind the waterfall is worn away creating a hollow cave like structure that is called the rock shelter. The rocky ledge sends down tumbles and boulders into the stream bed and plunge pools. The waterfall erosion starts again breaking the boulders down of the previous left rocks.
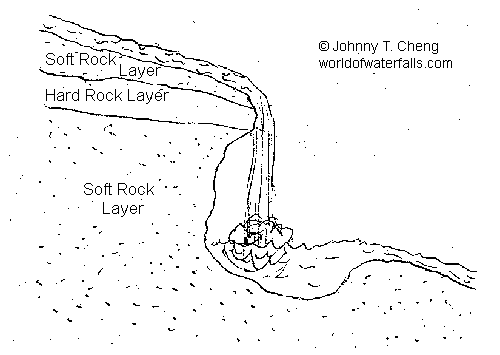
Basic Waterfall Formation Principle