This study guide covers the muscular system, skeletal system, joints, and common disorders in detail. Written in notes style, it highlights important concepts for quick learning and exam preparation.
1. Types of Muscles
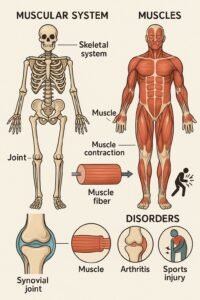
Skeletal Muscles
- Location: Attached to bones
- Control: Voluntary (under conscious control)
- Structure: Striated, multinucleated (nuclei at periphery)
- Movement: Fastest, enables running, jumping, lifting, waving
- Attachment: Connected via tendons or flat aponeurosis
Smooth Muscles
- Location: Internal organs (stomach, intestines, blood vessels)
- Control: Involuntary (automatic)
- Movement: Slowest, controls digestion and blood flow
- Structure: Spindle-shaped, unstriated, single nucleus
Cardiac Muscles
- Location: Found only in the heart
- Control: Involuntary
- Movement: Moderate speed, maintains heartbeat
- Structure: Striated, branched, single or double central nucleus
Strongest Muscle: Masseter (jaw muscle) – can exert up to 90 kg force.
General Features of muscles: Excitability, Contractility, Extensibility, Elasticity. Muscles make up 40–50% of body weight. Human body has 639 muscles, with maximum (180) in the back.

2: Structure and Mechanism of Muscle Contraction
Microscopic Structure
- Muscle bundles (fascicles) covered by fascia
- Muscle fiber: multinucleated, surrounded by sarcolemma, contains sarcoplasm
- Sarcoplasmic reticulum: Stores calcium ions
- Myofibrils: Parallel filaments with alternating light and dark bands
- I-band: Actin (thin filaments)
- A-band: Myosin (thick filaments)
- Z-line: Anchors thin filaments
- M-line: Anchors thick filaments
- Sarcomere: Functional unit of contraction
- H-zone: Central region of A-band with only myosin
Contractile Proteins
Actin: Thin filament formed of F-actin (polymer of G-actin), associated with tropomyosin and troponin which regulate myosin binding.
Myosin: Thick filament made of meromyosin. Head region (HMM) has ATPase and actin binding site, tail (LMM) forms backbone.
Sliding Filament Theory
- Nerve impulse reaches neuromuscular junction.
- Acetylcholine released, generating action potential.
- Calcium ions released into sarcoplasm.
- Calcium binds troponin → exposes actin binding sites.
- Myosin heads attach to actin using ATP → cross-bridge formation.
- Actin filaments slide inward → Sarcomere shortens.
- I-band shortens, A-band remains constant.
- ATP binding breaks cross-bridge, cycle repeats.
- Impulse stops → calcium reabsorbed → muscle relaxes.
Red vs White Fibers
- Red fibers: High myoglobin, more mitochondria, aerobic, fatigue-resistant
- White fibers: Low myoglobin, fewer mitochondria, anaerobic, fatigue quickly
3. Skeletal System

The skeletal system provides structure, support, movement, and protection. It consists of 206 bones and cartilages.
Axial Skeleton
- Total bones: 80
- Skull: 22 bones (8 cranial + 14 facial)
- Vertebral column: 26 vertebrae – cervical (7), thoracic (12), lumbar (5), sacrum (1), coccyx (1)
- Sternum: Flat bone in chest center
- Ribs: 12 pairs – 7 true ribs, 3 false ribs, 2 floating ribs
Appendicular Skeleton
- Upper limb: 30 bones – humerus, radius, ulna, carpals (8), metacarpals (5), phalanges (14)
- Lower limb: 30 bones – femur, tibia, fibula, tarsals (7), metatarsals (5), phalanges (14), patella
- Pectoral girdle: Clavicle + scapula; scapula forms shoulder joint with humerus
- Pelvic girdle: Ilium + ischium + pubis; forms acetabulum for femur
4. Joints
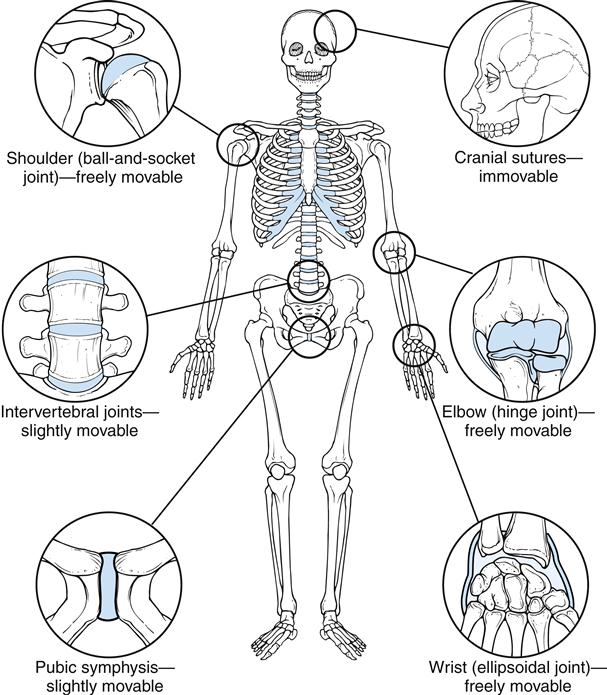
Definition: Junction between two bones or bone and cartilage. Function is movement and support.
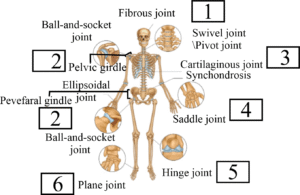
Types of Joints
- Fibrous joints: Immovable (e.g. skull sutures)
- Cartilaginous joints: Limited movement, connected by cartilage (e.g. vertebrae)
- Synovial joints: Fluid-filled cavity, free movement
- Ball and socket: shoulder, hip
- Hinge: knee, elbow
- Pivot: atlas and axis
- Gliding: between carpals
- Saddle: thumb joint
5. Musculoskeletal system Disorders
Sports Injuries
- Causes: overtraining, poor technique, lack of warm-up, weak muscles
- Examples: muscle strain, shin splints, shoulder injury, lower back pain, tennis elbow, ankle sprain, groin strain
- Treatment: RICE (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation), stretching, proper shoes
Aging Effects
- Bone density decreases → osteoporosis risk
- Cartilage becomes less flexible → osteoarthritis
- Muscle loss (sarcopenia) after age 30
Processed Food Impact
- High sugar, fat, sodium → inflammation, muscle weakness
- Reduces recovery, increases insulin resistance
Other Disorders
- Myasthenia gravis: Autoimmune, causes muscle weakness
- Muscular dystrophy: Genetic, progressive muscle degeneration
- Tetany: Low calcium → muscle spasms
- Arthritis: Joint inflammation
- Osteoporosis: Weak brittle bones
- Gout: Uric acid crystals in joints
- Fibromyalgia: Chronic muscle pain, fatigue
Glossary
- Actin: Thin contractile protein filament in muscles
- Myosin: Thick filament with ATPase activity
- Sarcomere: Functional unit of contraction
- Sarcolemma: Plasma membrane of muscle fiber
- Sarcoplasmic reticulum: Stores and releases calcium ions
- Neuromuscular junction: Synapse between motor neuron and muscle fiber
- Acetylcholine: Neurotransmitter triggering muscle contraction
- Tropomyosin: Protein covering actin sites during rest
- Troponin: Protein controlling actin-myosin binding
- Tendon: Fibrous tissue connecting muscle to bone
- Osteoporosis: Age-related bone weakening
- Osteoarthritis: Degeneration of cartilage at joints
- Fibromyalgia: Chronic muscle pain disorder
- Sarcopenia: Age-related muscle mass loss
- Ball and Socket Joint: Synovial joint allowing multi-directional movement
Question and Answers
Musculoskeletal System – Important Short Answer Questions (SAQs)
Musculoskeletal System – Important Questions and Answers (LAQs)